

According to the Oryx Project, the Russian military has suffered significant losses in Ukraine, including 1,905 tanks, 2,316 infantry fighting vehicles, and 586 self-propelled and towed artillery pieces. The Russian industry is eager to provide new vehicles to the front as soon as possible to replace the lost ones, but clearly there is a shortage of military equipment. Additionally, the formation of new units during the six months of mobilization poses another challenge as they require equipment as well. The Soviet-era equipment and weapons depots are being utilized to address this issue. The Insider has provided noteworthy examples of weapons that are often several times older than the soldiers who use them in combat.
Content
The “triumphant return” of the T-62
The “Stalin quality” of the D-1 howitzer
The “maneuverable and mobile” BTR-50
The MT-12 cannon – Vitaly Milonov's choice
The uncompetitive T-54 and T-55 tanks
The T-34 and the IS-3: fakes and memes
The “triumphant return” of the T-62
During the Cold War era, the T-62 and its various modifications were among the most widely manufactured Soviet tanks. Production began in 1962, and the T-62 first saw combat in 1968 during the Czechoslovakia occupation. The tank was deployed in numerous conflicts across the Middle East and Africa, as well as in the Soviet-Afghan war and two Chechen wars. The Russian Army's last use of the T-62, before it was retired, occurred during the 2008 conflict with Georgia.
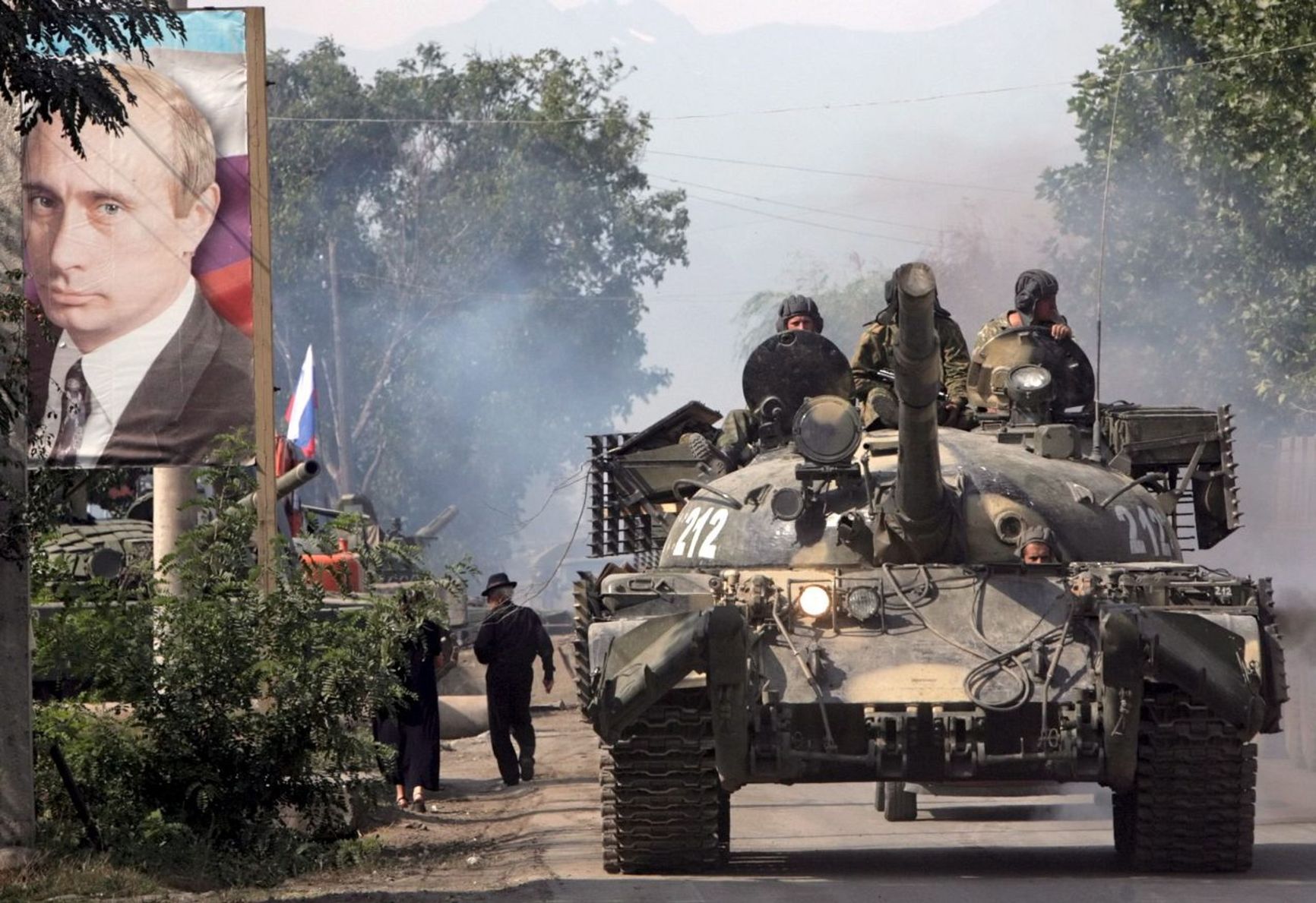

A Russian T-62 in Tskhinvali in August 2008
Maxim Shippenkov/EPA/dpa
Russia first unsealed the T-62 depots in 2017, and those tanks ended up in Syria to aid Bashar al-Assad's forces. Initially, the tanks were intended to support the Russian air group as part of the 5th Corps, a coalition created specifically for ground support. The supplied tanks were the T-62M version upgraded in the 1980s, which featured additional armor on the turret, colloquially known as “Ilyich's eyebrows” in reference to General Secretary Brezhnev. The tanks, judging by the DShB (VAB) markings, were also present in the arsenal of the Wagner PMC's “volunteer assault battalions.” As Prigozhin was already on poor terms with the Russian Defense Ministry at the time, obtaining modern equipment proved more difficult for him.

Wagner PMC's T-62M in Syria
twitter.com/Mortis_Banned
During mobilization preparations, rehearsals were conducted to bring the T-62s out of storage. This may explain why they were deployed to the front rather swiftly, with the first train carrying these tanks arriving in Melitopol at the end of May 2022. Subsequently, the majority of these tanks were deployed in Donbass and on the right bank of the Dnieper River.

T-62Ms on a military train in Melitopol, spring 2022
telegraf.com.ua
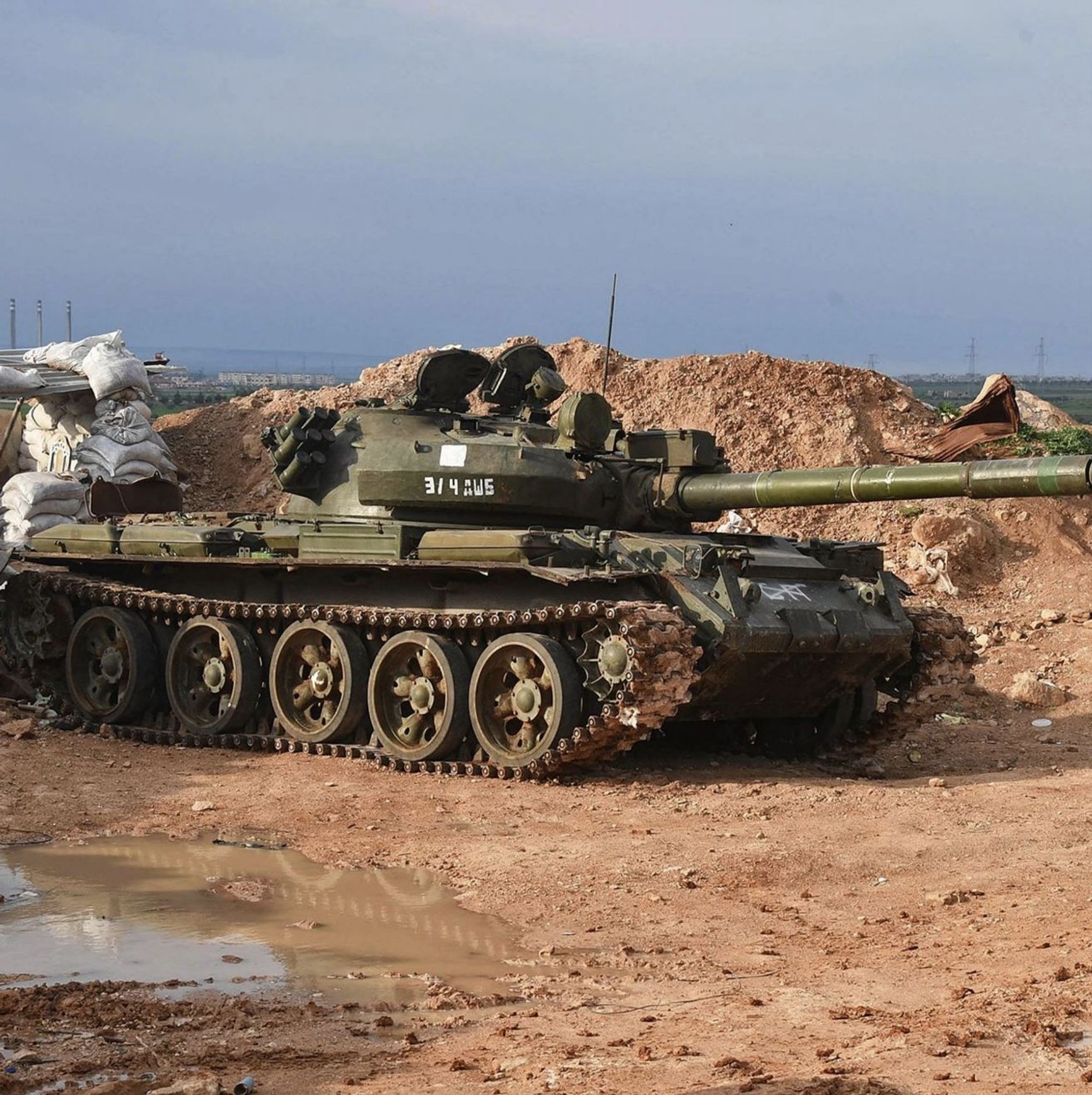
According to military historian Bernhard Kast, the earlier T-62 models are not significantly inferior to the T-72s, which are also utilized in the conflict. However, these tanks have not performed well in combat, with numerous T-62s being destroyed or captured, particularly during the Ukrainian counterattack in the Kherson area. Currently, the Ukrainian military is primarily utilizing the captured tanks for training purposes or as a base for repair and recovery vehicles.

A Ukrainian repair and recovery vehicle based on the T-62
t.me/btvt2019
State Duma member Andrei Gurulev discussed a plan to upgrade 800 T-62 tanks over three years at a tank repair plant in Transbaikalia on his Telegram channel in November 2022. The tanks are currently being fitted with dynamic protection units and relatively modern thermal imaging devices. However, progress has been slower than anticipated. Five months later, Gurulev revealed that the plant had only shipped “a battalion and a few more tanks,” indicating no more than 30 vehicles had been upgraded so far.
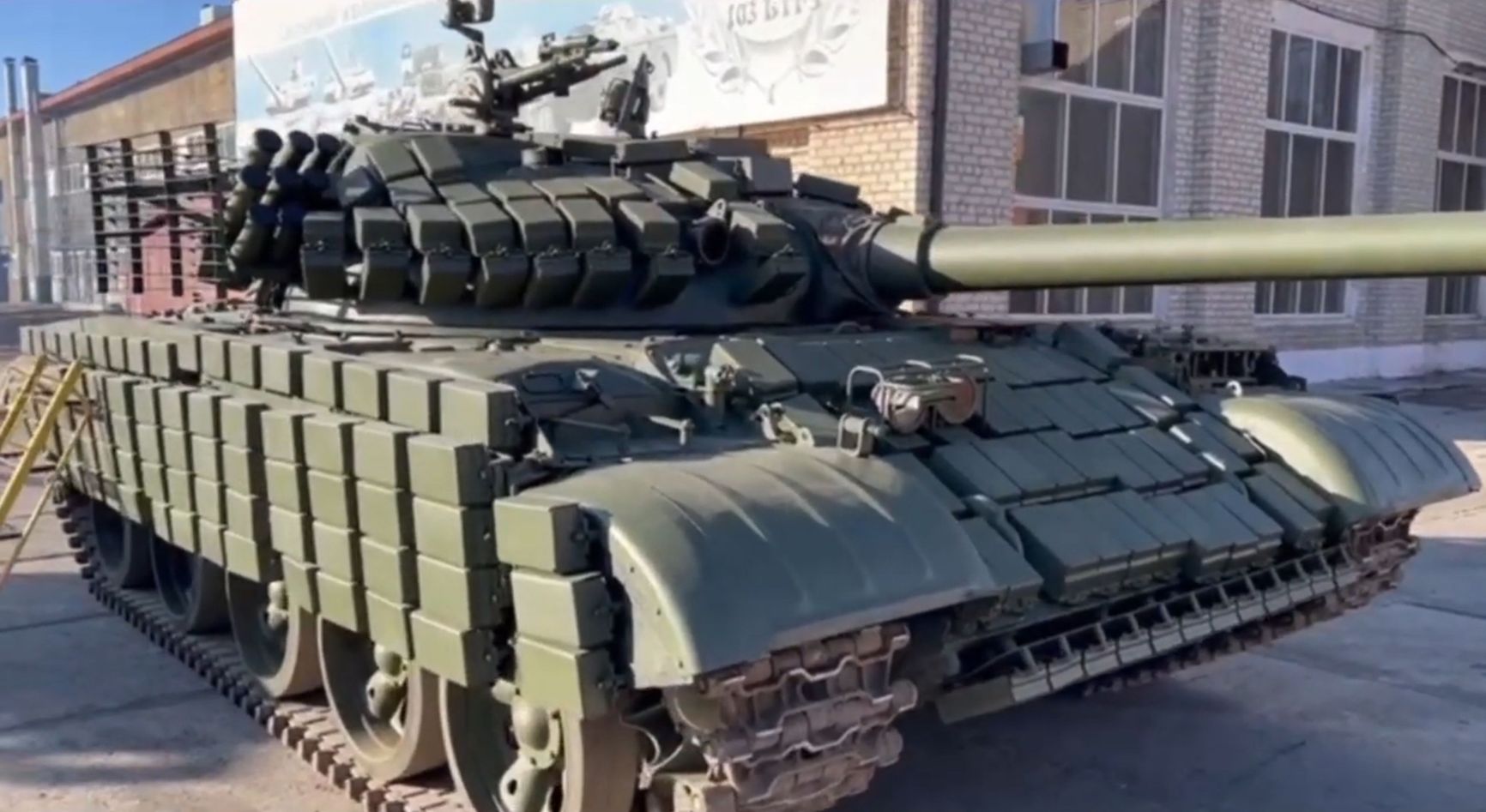

A modernized T-62, 2023 model, at the Chita plant
mil.in.ua
The “Stalin quality” of the D-1 howitzer
The 152mm D-1 howitzer from 1943 serves as a remarkable example of armament utilized in the Russian-Ukrainian war, which was previously literally wielded by “grandfathers” in battle. This howitzer saw extensive use during the final phase of World War II and remained in service with the Soviet army until the 1980s. As of 2021, The Military Balance reported that the Russian Federation possessed 700 of these guns in storage.
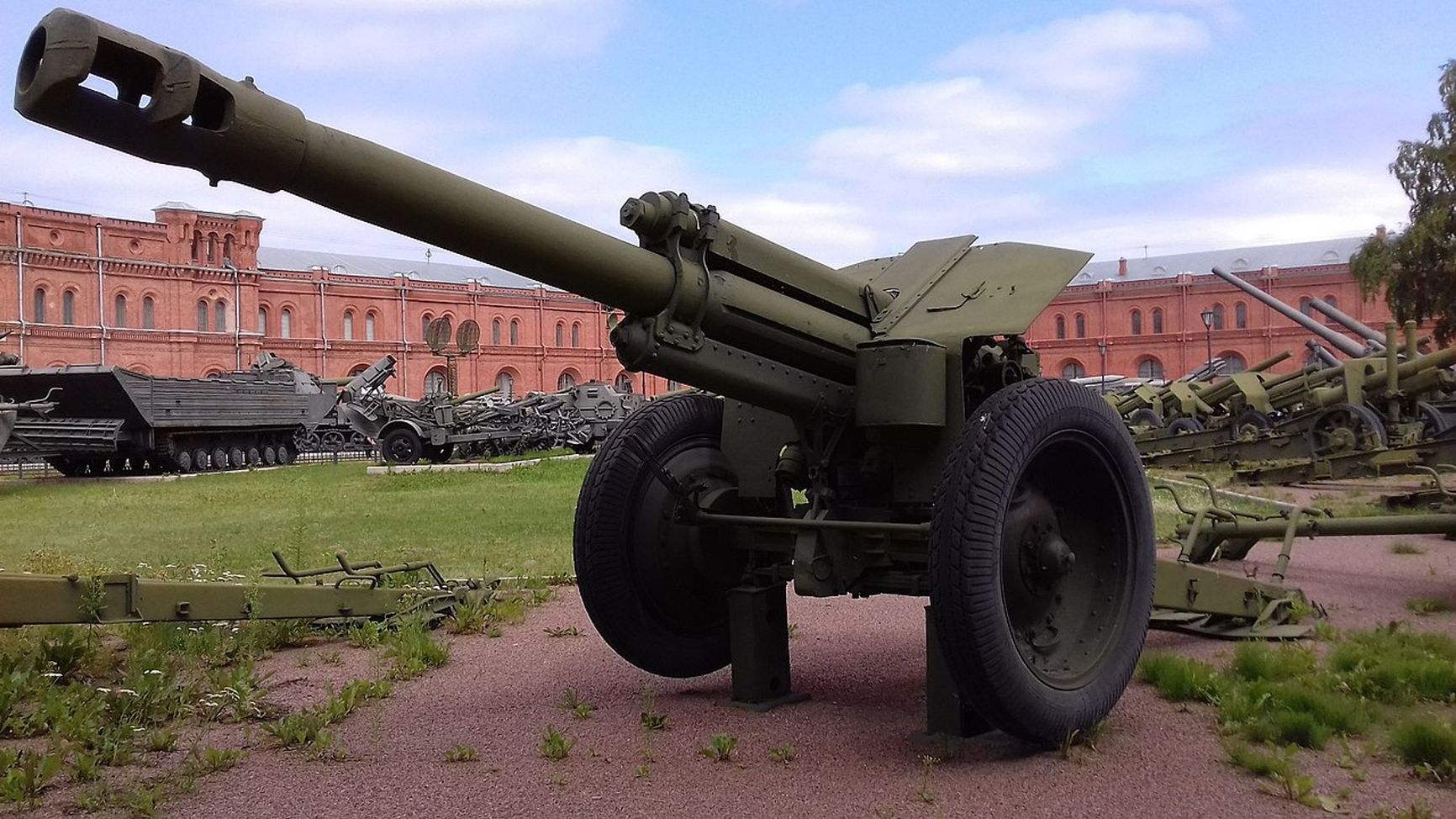

A D-1 howitzer in the artillery museum in St. Petersburg
wikipedia.org
Andrei Morozov, a pro-Russian blogger and an “LNR” serviceman, shared on his Telegram channel that the D-1 howitzer began to arrive in troops in August 2022. The older 152-mm shells were intended for use with these howitzers. However, it was not until October that the first footage of this type of howitzer in Donbass emerged. Later, Morozov published combat footage of the D-1, which seemingly dates back to the summer of 2022.
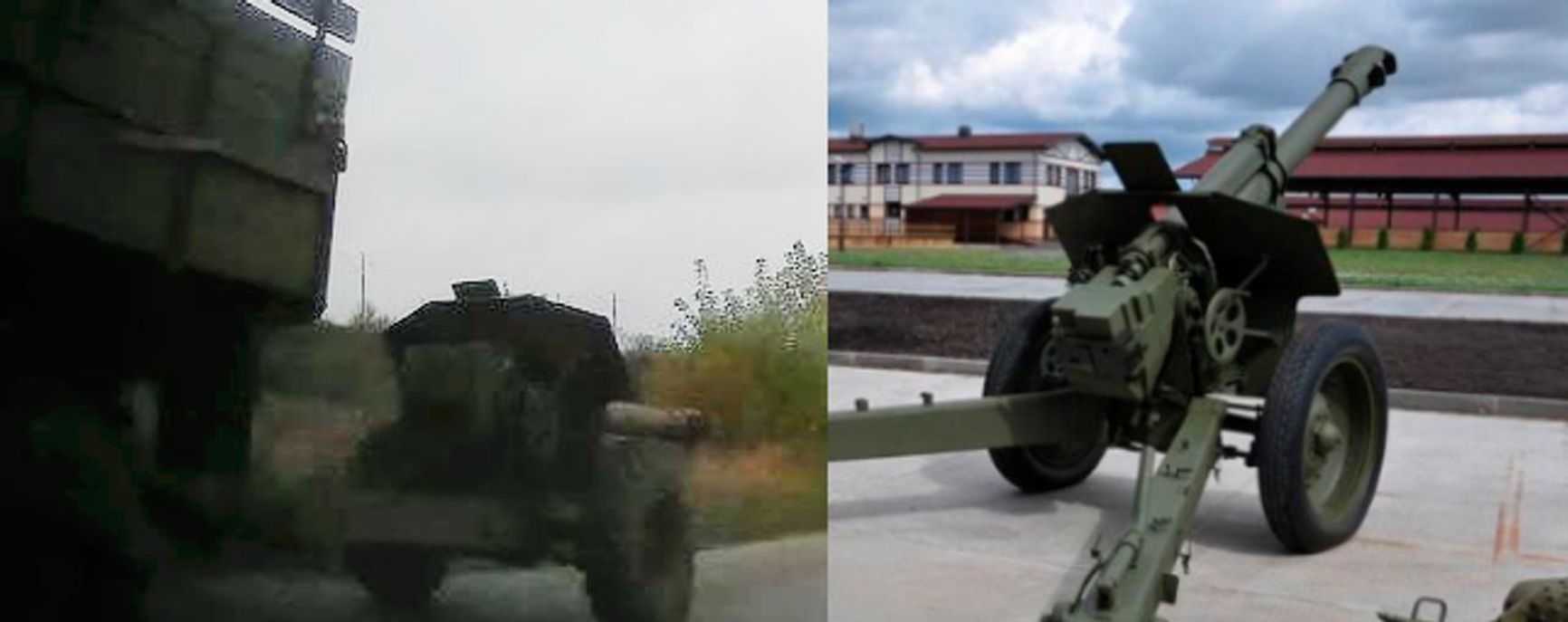

A D-1 in the occupied territory of Ukraine in comparison with the reference photo
Ukraine Weapons Tracker
The late “war correspondent” Vladlen Tatarsky ironically pointed out the “Stalin quality” of the D-1. This is indeed ironic since the D-1 howitzer has a range half as long as the 2A65 Msta-B, which was the most widely produced towed gun in the arsenal of the Russian Armed Forces of the 1970s before the full-scale war.
The “maneuverable and mobile” BTR-50
During World War II, the Soviet industry did not manufacture armored personnel carriers, so the Red Army had to rely on Lend-Lease supplies or often rode into battle on the armor of tanks and self-propelled guns. After the war, the USSR's military-industrial complex began to catch up, and in 1954, the first tracked armored personnel carrier, the BTR-50, was introduced into service. The early versions of this armored personnel carrier did not have a troop compartment roof (which could hold up to 20 people) and could also carry a light gun or mortar, which could be fired from it, particularly while waterborne. However, the current armored fighting vehicles used have a troop compartment roof.
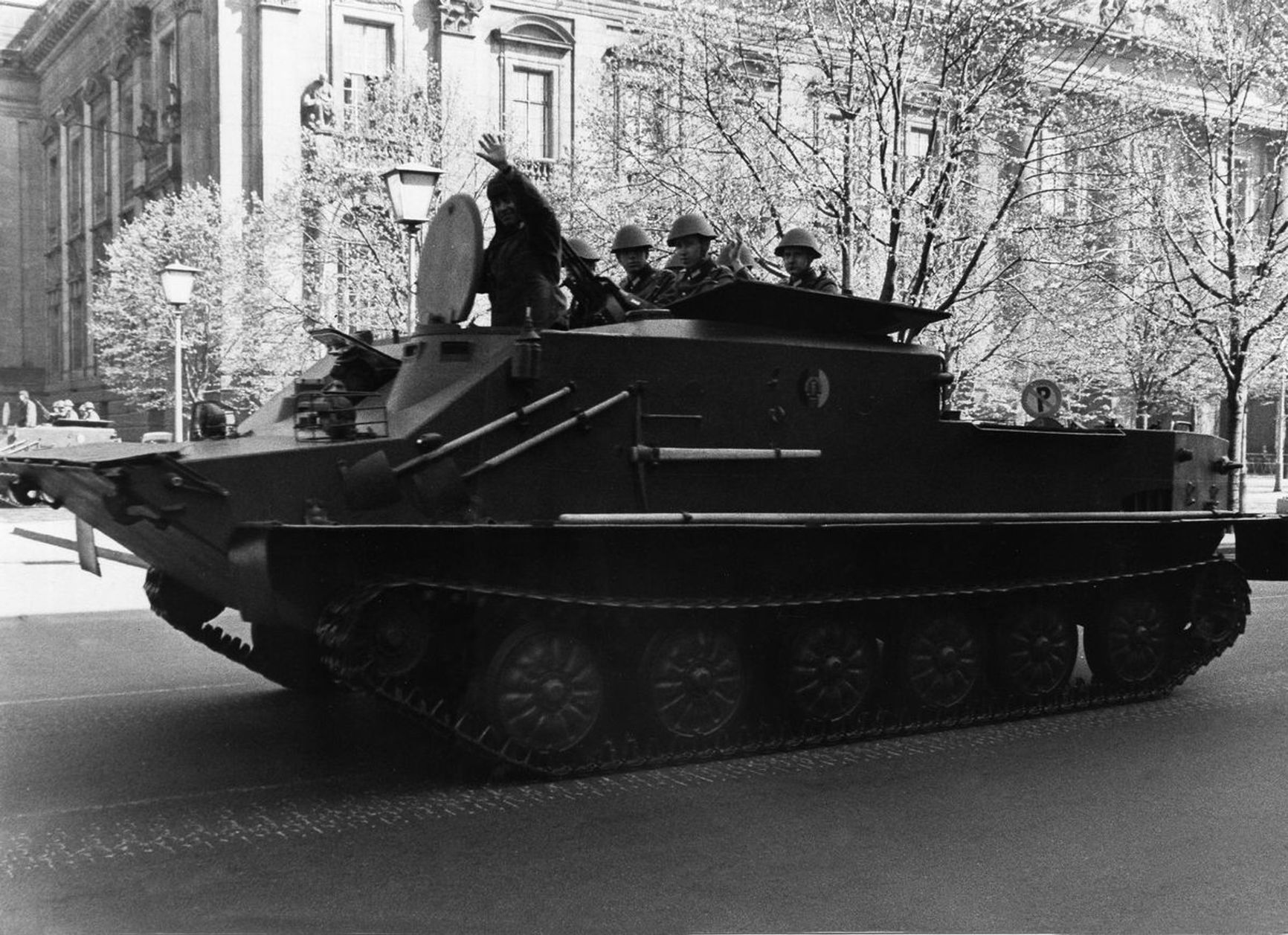

An APC-50 of the GDR National People's Army
ullstein bild/Getty Images
During the Arab-Israeli wars, the BTR-50s were widely utilized by both opposing sides. Israel was able to acquire significant numbers of these armored vehicles as well as other Soviet-made armored vehicles that had been provided to Arab countries. Prior to the full-scale war in Ukraine, efforts were made to upgrade the BTR-50, but the outcome of this project is currently unknown.
The initial image of the BTR-50 within the “SMO zone” was released by Kirill Fedorov, a pro-Russian blogger. Later, the Ukraine Weapons Tracker project posted a photo of the armored personnel carrier, which appeared to have been in service for quite some time. Experts have identified the BTR-50PU in the picture as a commander's version of the vehicle, but it remains unclear how it will be utilized. Analysts believe that the appearance of Russian BTR-50PU in the Ukrainian war can be attributed to the scarcity of armored vehicles, including multipurpose MT-LB tractors with light armor.
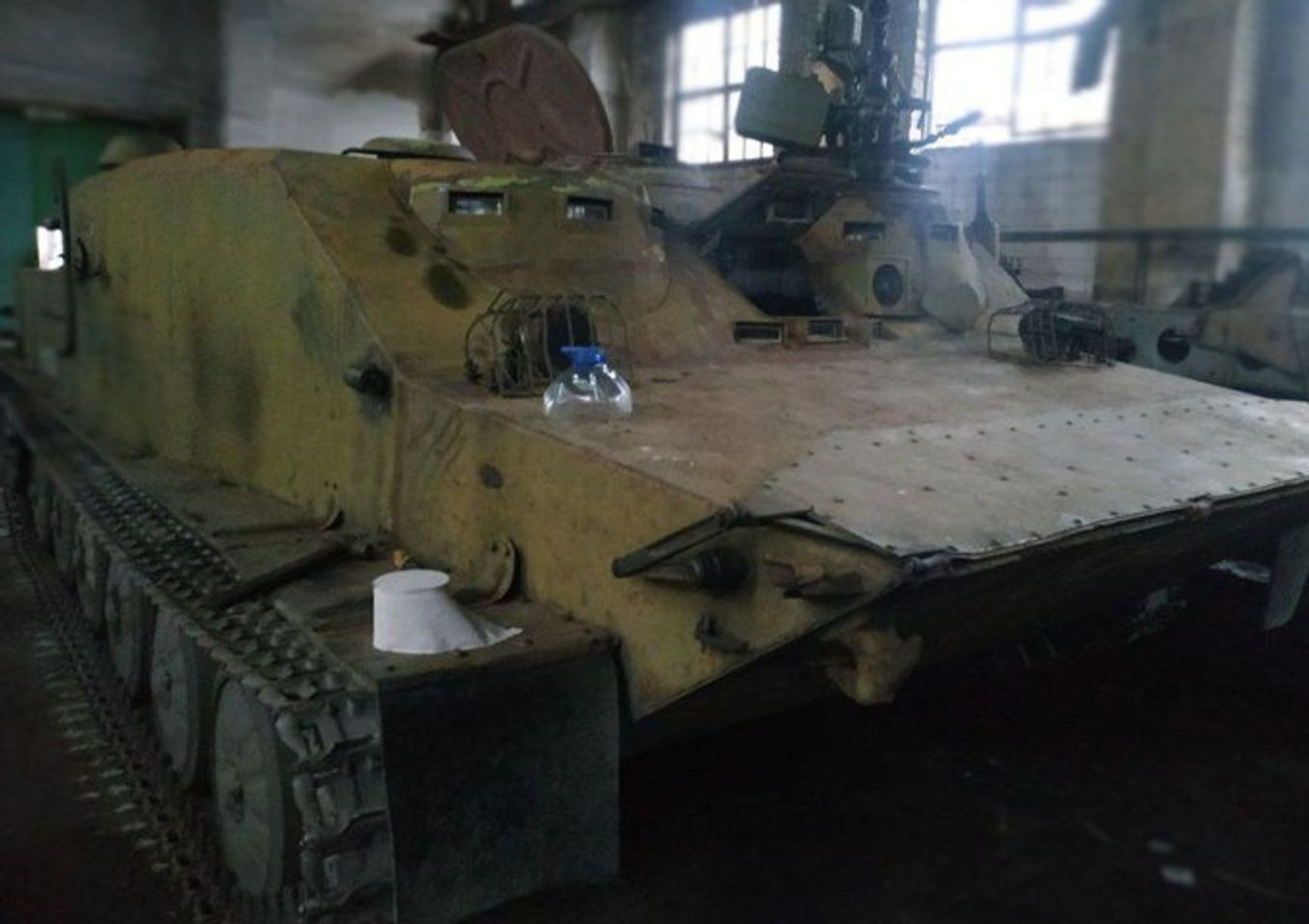

A BTR-50 somewhere in the occupied territory of Ukraine
Ukraine Weapons Tracker
The appearance of the BTR-50 at the front was viewed with a mix of pessimism and resignation by most Z-channels. However, some argued that it would give them an advantage in maneuverability and mobility over the AFU. It should be noted that the specific engine power of the BTR-50, measured in horsepower per ton, is only half that of the MT-LB or American M113 armored personnel carriers that are widely supplied to the AFU. Nonetheless, due to the scarcity of mechanized resources on both sides of the conflict, the BTR-50 could still be useful in the immediate rear - for transporting personnel and ammunition, as well as for evacuating the wounded.
The MT-12 cannon – Vitaly Milonov's choice
Anti-tank guns emerged as one of the primary ways to combat tanks on the battlefield since the introduction of tanks. These guns were typically used to directly hit tanks with armor-piercing shells. They played a significant role in World War II, but were eventually supplanted by lightweight and mobile anti-tank grenade and rocket launchers. Despite this, the development of anti-tank guns continued post-war, with the 100mm T-12 being adopted for service in 1955.
The Conflict Intelligence Team (CIT), which monitors the Russian military using open sources, recently shared a photo of a T-12 cannon in Yevpatoria, occupied Crimea. The fact that the T-12 is being towed by a military truck suggests that it is not intended for a museum or parade but is likely headed to the front or one of the defense lines being established in Crimea.

A 1955 MT-in Yevpatoria
CIT
As of now, there is no information available on whether the T-12 has been used in combat in Ukraine. However, the MT-12 Rapira underwent modernization in the 1970s and is currently used by both sides as a conventional artillery gun. For instance, Vitaly Milonov, a member of the State Duma, served in the crew of such a gun for some time. The Ukrainian military transforms the MT-12 into improvised self-propelled artillery units by mounting them on the MT-LB multi-purpose transporter-tractor. One such vehicle is visible in a video by the Ukrainian band Kozak System. Additionally, the Ukrainian military has employed the MT-12 as intended, using it to destroy Russian vehicles.
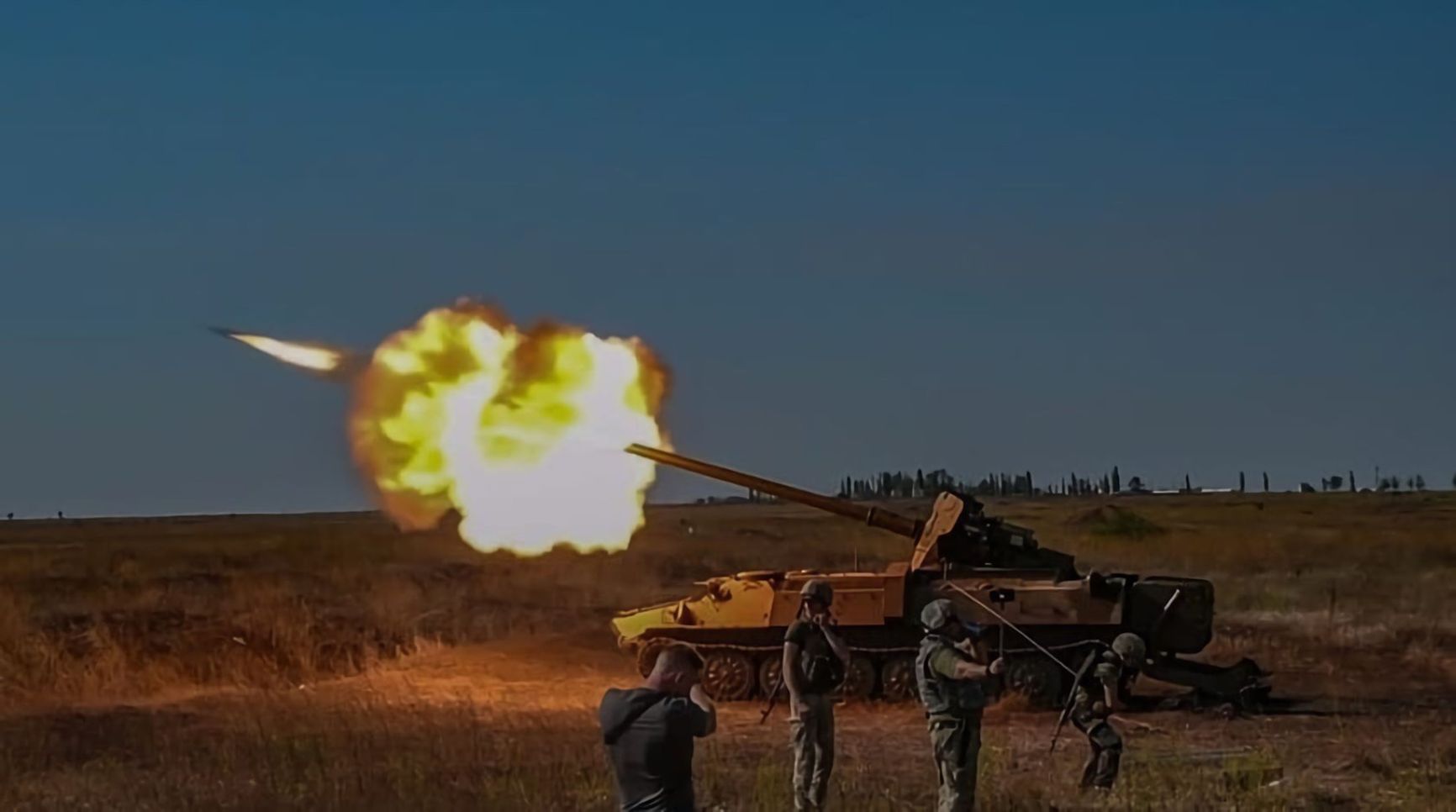

A MT-LB-12 in service with the AFU
twitter.com/UAWeapons
The uncompetitive T-54 and T-55 tanks
The T-54 and its upgraded version, the T-55, are iconic tanks that symbolized the Cold War. These tanks were first produced in 1945, and the T-55, which looks identical to the T-54, was later introduced. The T-62, which was used in combat for the first time during the suppression of the anti-communist Hungarian Revolution in 1956, also shares similarities with these tanks.
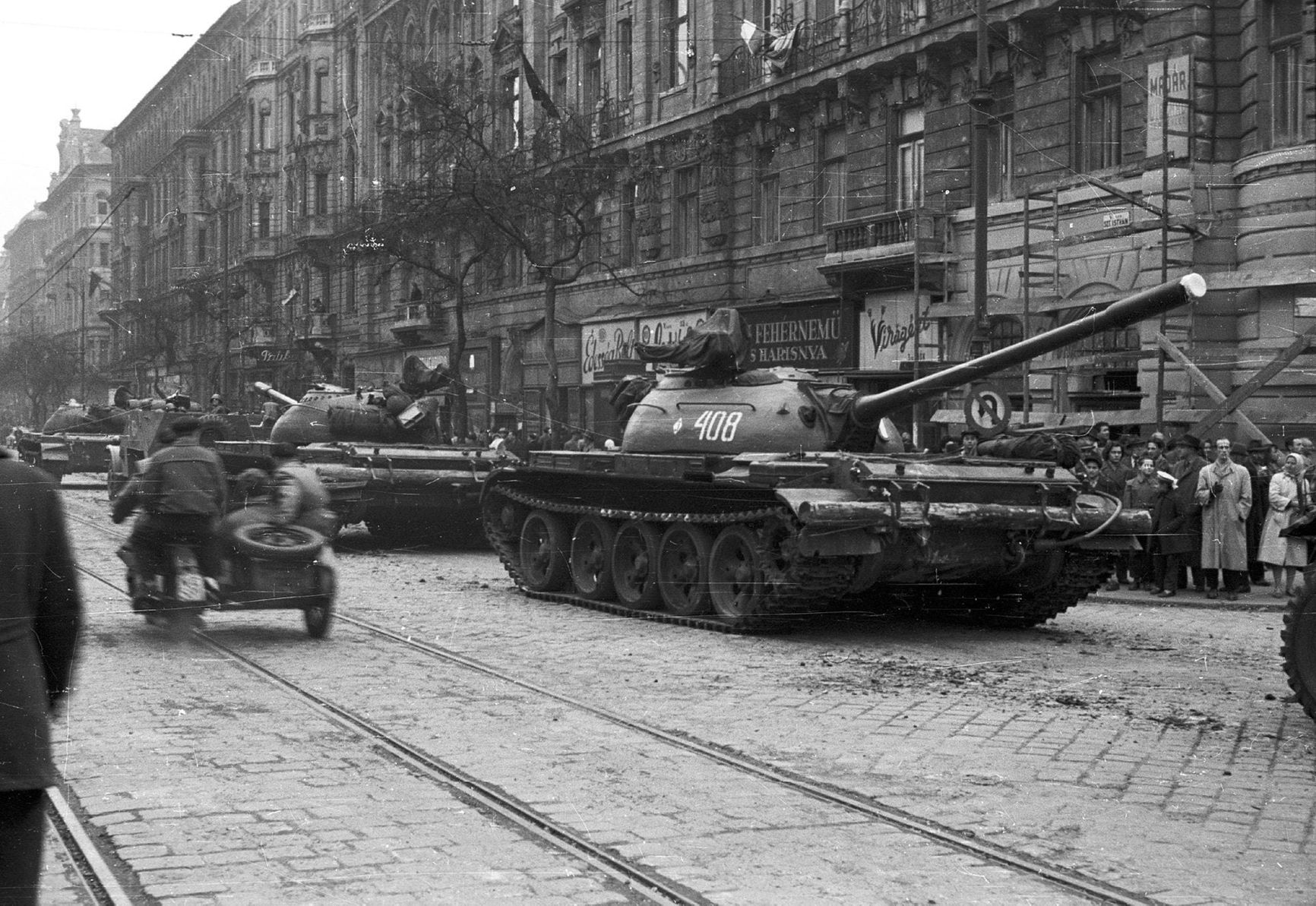

A convoy of Soviet T-54 tanks in Budapest, 1956
reddit.com/r/TankPorn
The T-54 and T-55 tanks have been involved in nearly all major military conflicts since their creation, and are still in use today. One example is their use by the Armed Forces of Sudan in their conflict with the Rapid Support Forces.
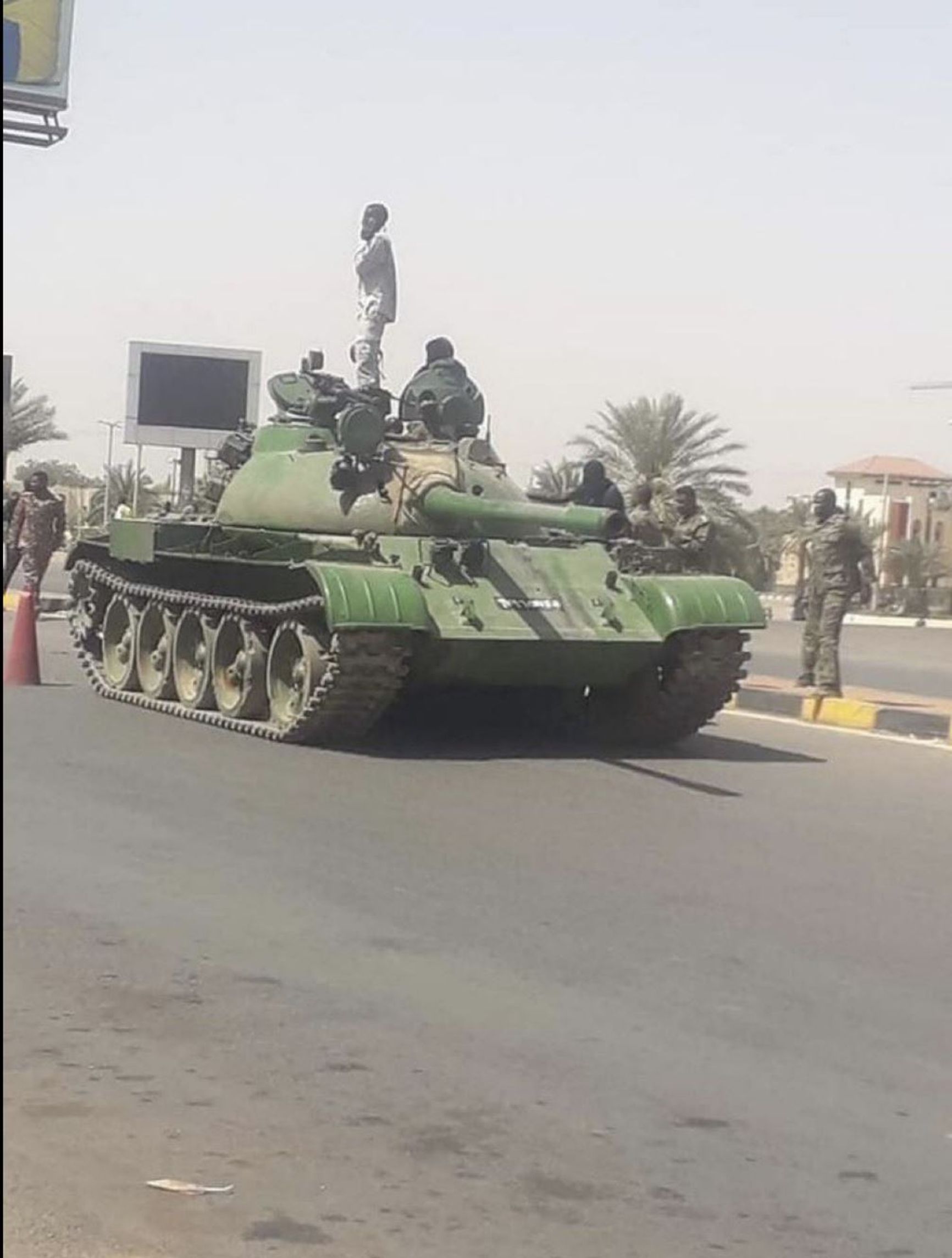

A T-54/55 in Sudan, April 2023
twitter.com/WWIIIAR
It is noteworthy that in the midst of the large-scale invasion of Ukraine, the Ukrainian Armed Forces were the first to receive T-55 tanks. These tanks were the result of a Slovenian deep modernization of the M-55S, which now features a new gun with a NATO caliber of 105mm and a modern computerized fire control system. According to The Insider's sources, one of the brigades prepared for the Ukrainian counterattack is equipped with these tanks, as well as American M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicles.
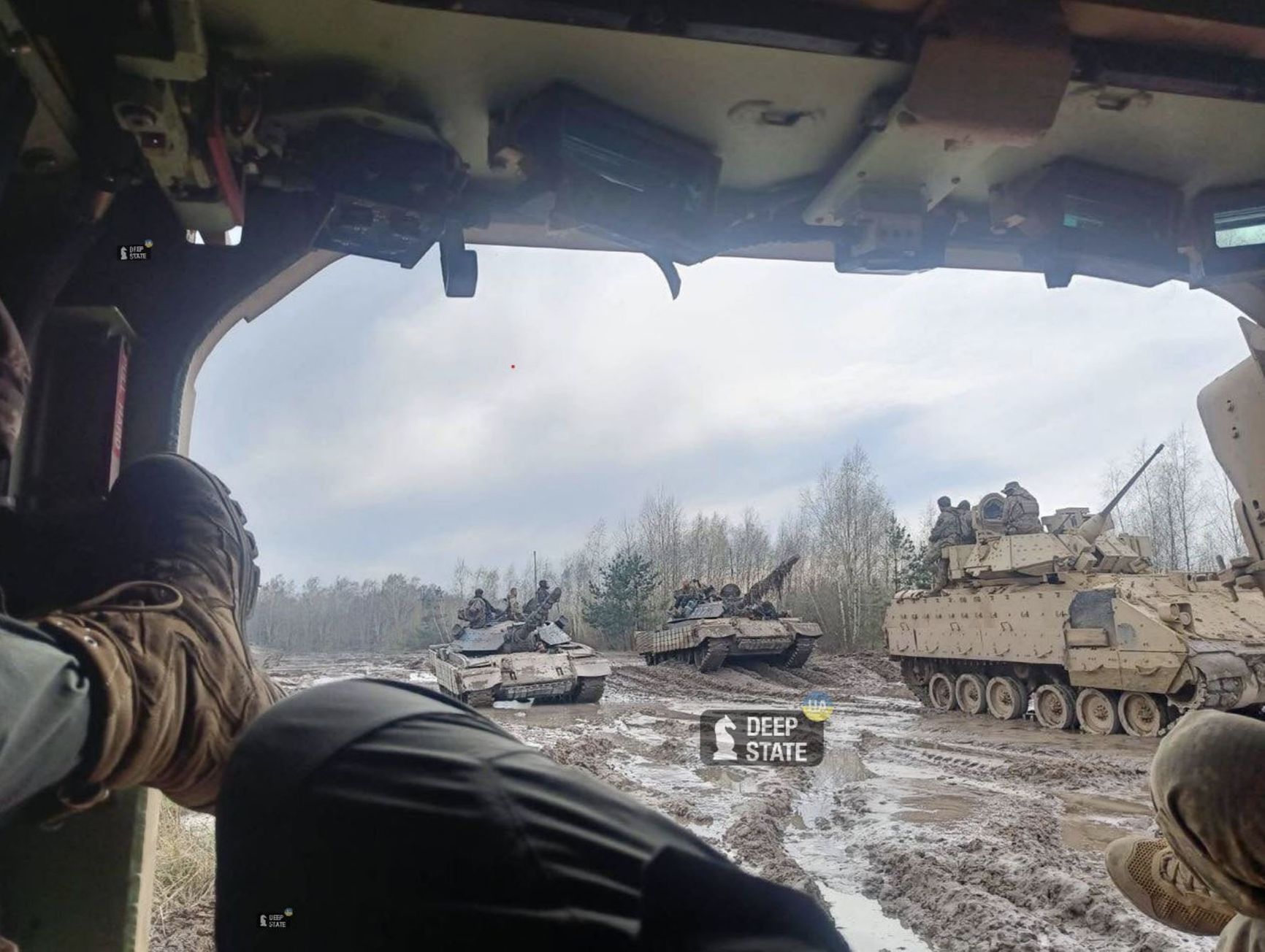

M-55S and M2 Bradley on a training ground somewhere in Ukraine
t.me/DeepStateUA
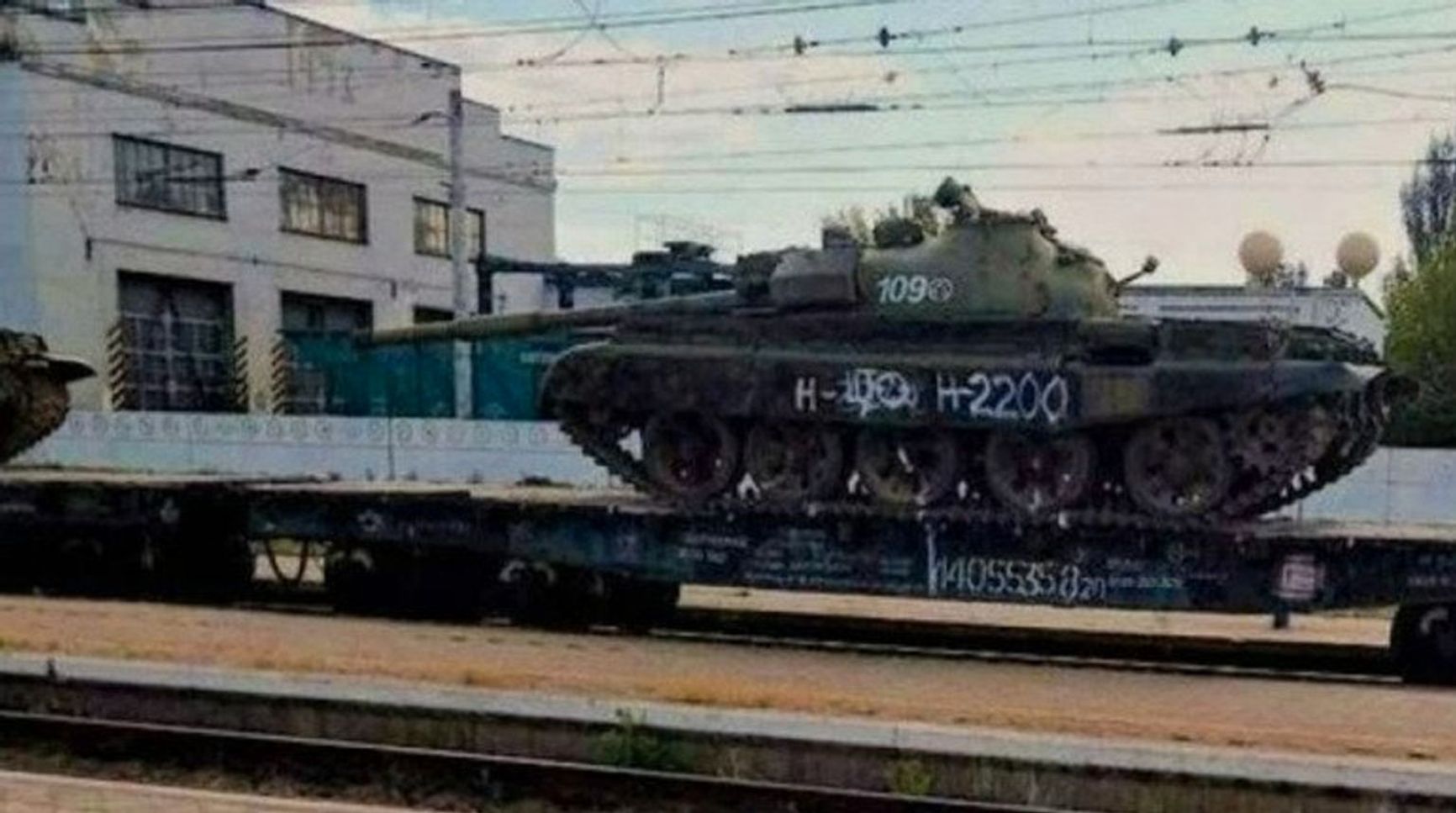
The T-55 tanks were officially withdrawn from service in Russia in 2010, although some were kept in storage. Recently, the Conflict Intelligence Team (CIT) were first to report that the T-54/55 tanks could be returning to the Russian forces, as they received photos of a trainload of these tanks in the Far East. Even the typically pessimistic pro-Russian blogger Andrei Morozov speculated that the T-54/55s would serve as spare parts donors for T-62s and BTS tractors. However, a photo of one of these tanks on the front line in the Zaporizhzhia region soon appeared, indicating that the Russians had decided to deploy them without any modernization.
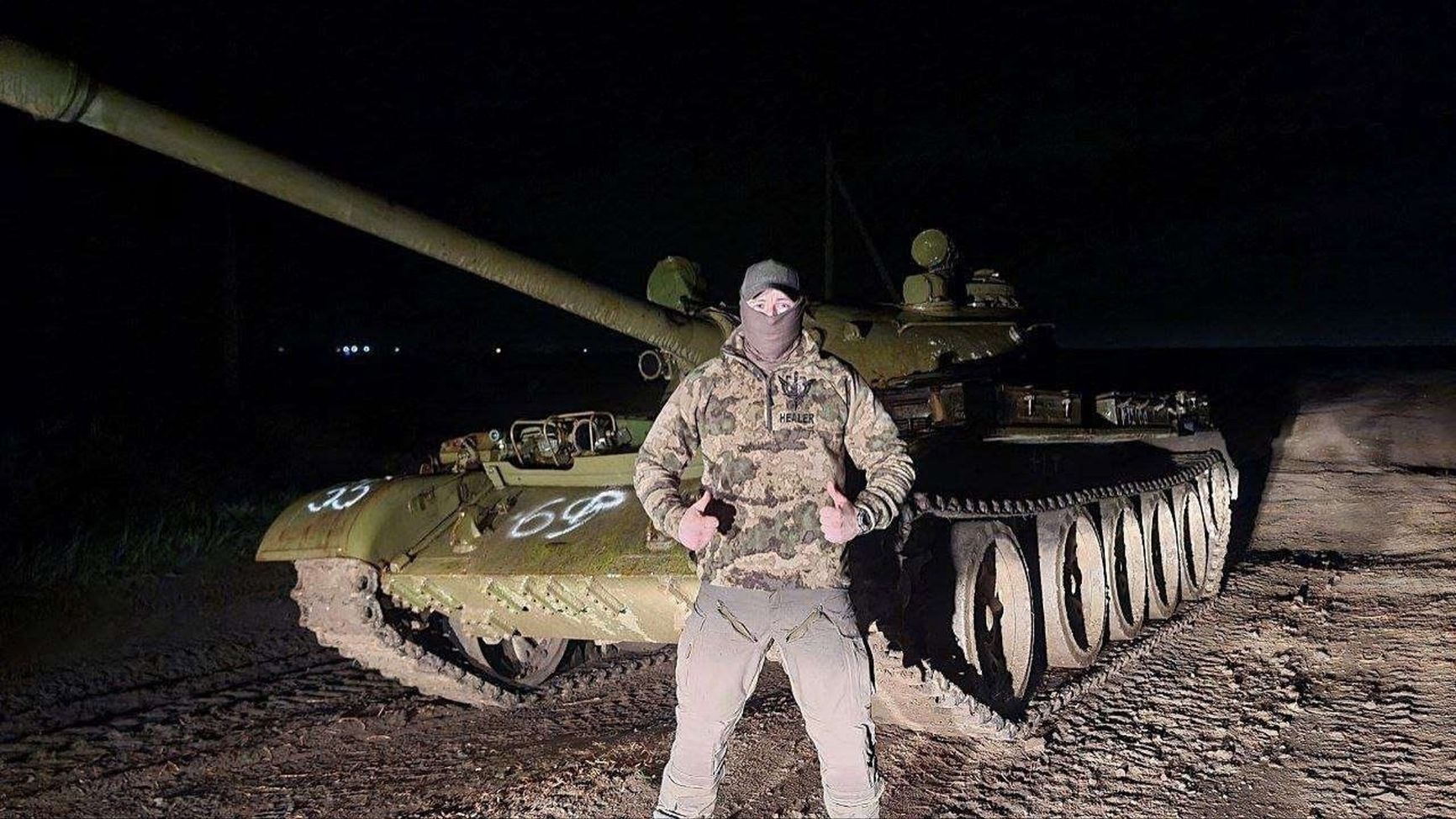

A Russian T-54/55 in the Zaporizhzhia region
t.me/cit_backup
The extensive legacy of the T-55 has garnered attention in military circles. Recently, a retired German soldier using the Twitter handle Der Gepardkommandant shared photos of T-54/55 and Leopard 1 tanks, the latter of which are also set to be supplied to the AFU. He referred to them as “natural rivals,” likely alluding to the possibility that these tanks would have confronted each other in Europe during a potential hot phase of the Cold War and may now encounter each other in actual combat.
It is worth noting that the A5 modification of the Leopard 1 surpasses the T-54/55 in terms of capabilities. The latter lacks advanced features such as fire control and gun stabilization systems, making it suitable only for use as an improvised artillery system or fixed firing point. However, even in this role, the T-54/55 would struggle to compete with vehicles such as the BMP M2 Bradley and the French “wheeled tanks” AMX-10 RC, which previously encountered the Iraqi T-55 during the Gulf War resulting in the defeat and retreat of Saddam's army.
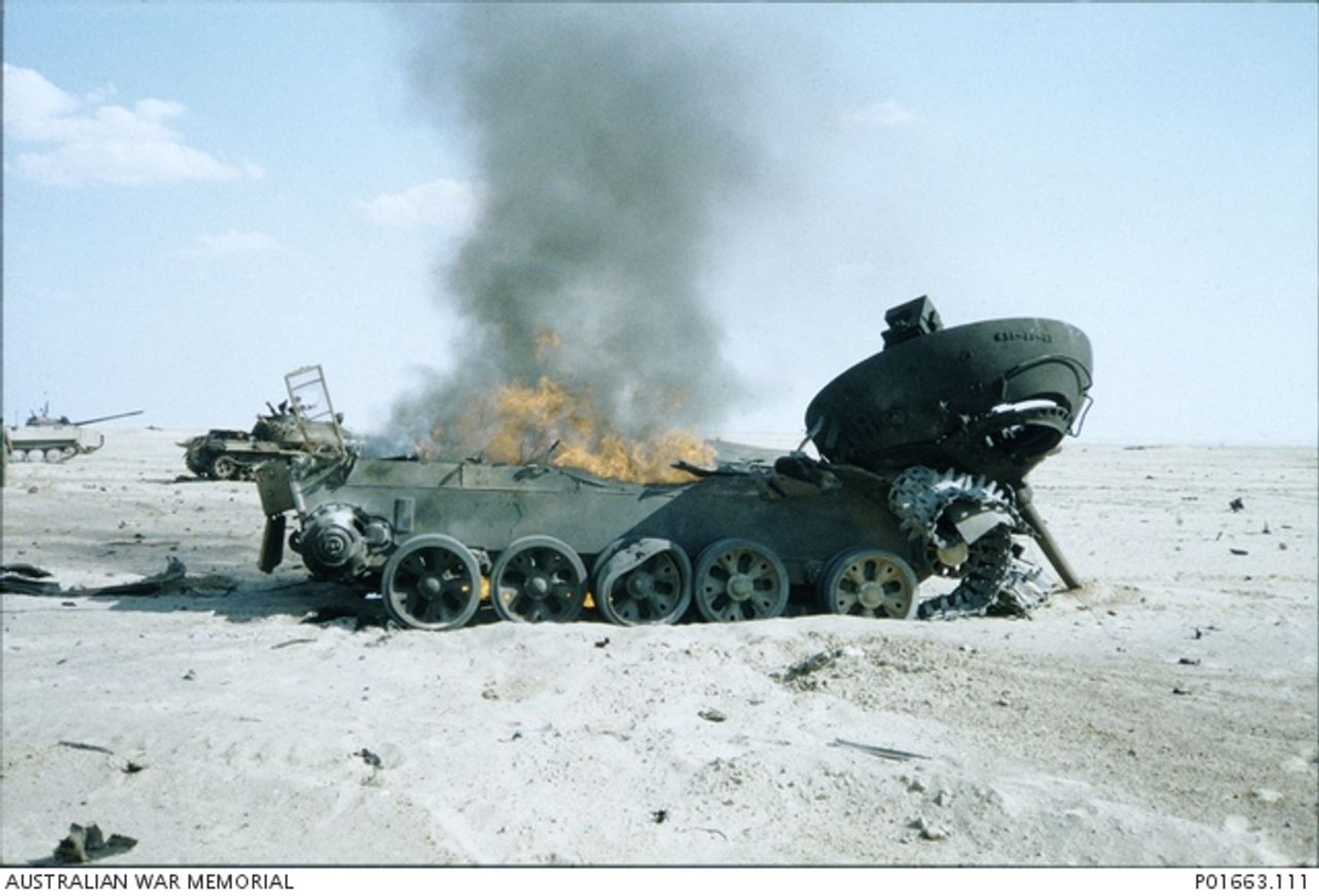

An Iraqi T-55 destroyed in the Gulf War
awm.gov.au
The T-34 and the IS-3: fakes and memes
The emergence of “new” outdated equipment in the Russian army has led to a flood of humorous comments on social media. Some Twitter users even jokingly suggest that Russia may soon resort to using the famous T-34 tanks, which are still displayed on parades and monuments across the country.
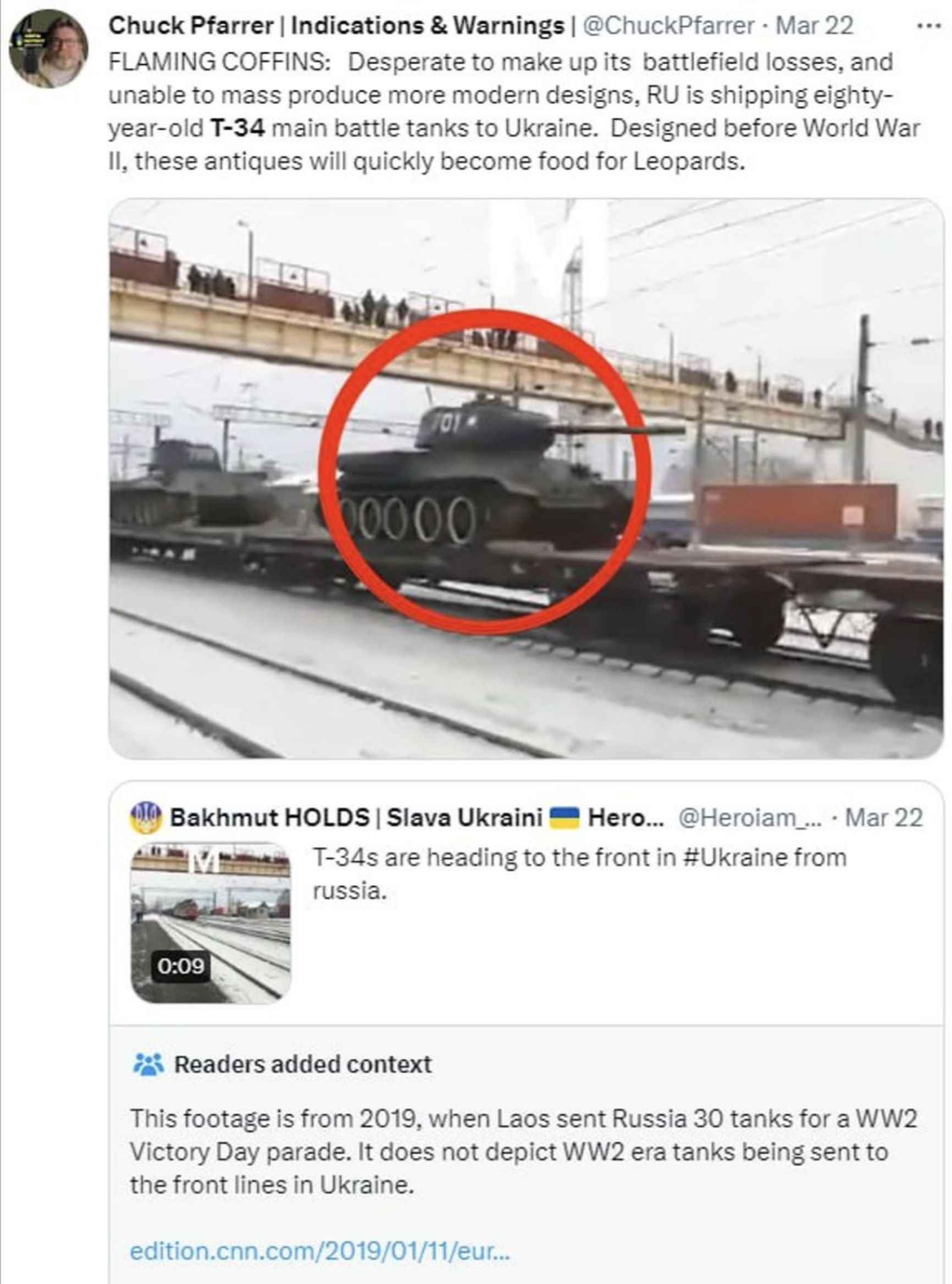
On the other hand, some sources suggest that these WWII-era tanks may actually be on their way to the frontlines. However, such claims have been found to be false, at least for now. A case in point is American analyst Chuck Pfarrer's tweet about the supply of T-34 tanks to the Ukrainian front, which became so popular that Twitter moderators had to add a disclaimer to it. As it transpired, the footage shared by Pfarrer was actually from 2019, when Russia received a shipment of operational T-34s from Laos for use in parades.
In March 2023, rumors emerged on social media claiming that IS-3 tanks were being sent to Ukraine. The IS-3 was developed towards the end of World War II but never saw combat. However, an analyst known as Status-6 refuted this information on Twitter, stating that the photo of the IS-3 that was circulating had been actually taken in 2021 or 2022. Additionally, there is no evidence to suggest that this equipment is actually being sent to Ukraine.
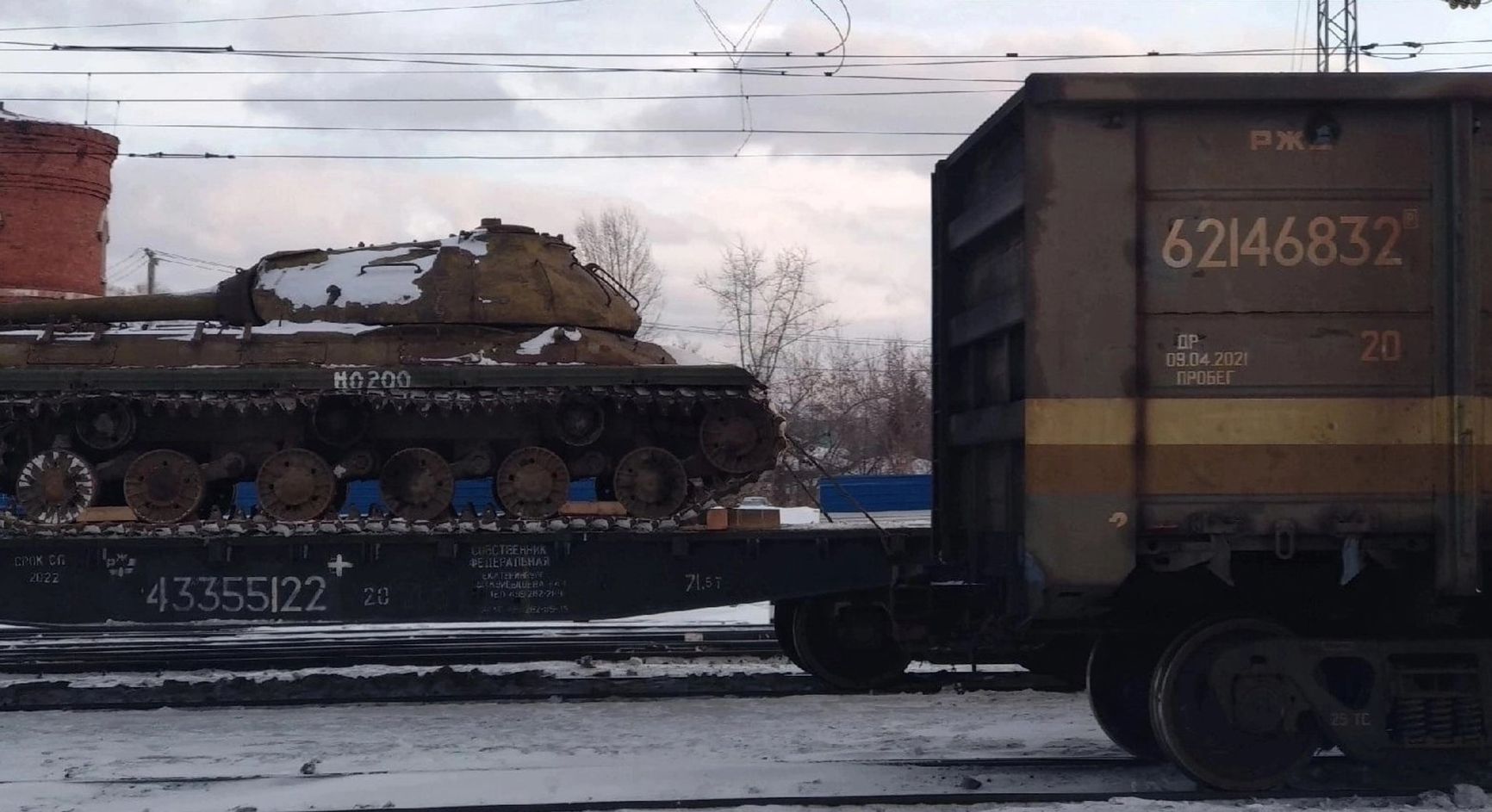

An IS-3 tank, which does not seem to be bound for Ukraine just as yet
twitter.com/ArmoredWar
Instead of spreading fake news, some Twitter users turned to creating memes. One example of this is when researcher Calibre Obscura shared a meme on April 1, 2023, claiming that Uralvagonzavod was planning to modernize fifty T-34 tanks by equipping them with new engines, automatic loaders, the Contact-1 dynamic defense (which became the subject of memes itself), and a plush figurine of Sergei Shoigu.

The 2023 T-34 by Calibre Obscura
twitter.com/CalibreObscura
The emergence of outdated military equipment in modern conflicts suggests a significant issue with the supply of artillery and combat vehicles to the Russian forces, although it is unlikely that T-34 tanks will be used in combat anytime soon. Most of the mentioned models, including T-54/55s and IS-3s, have limited usefulness on the battlefield in their current state. However, given the current circumstances where the Russian industry cannot meet the demands of a large-scale war, military personnel and mercenaries may increasingly resort to fighting “like their grandfathers” and continue to face significant losses.